. Algæ. Vol. I. Myxophyceæ, Peridinieæ, Bacillarieæ, Chlorophyceæ, together with a brief summary of the occurrence and distribution of freshwat4er Algæ . parent-axis. The branching isusually dichotomous, either in one plane or in alternate planes, althoughtrichotomous branching occurs in the basal part of Chlorodesmis comosa, inBoodleopsis, in Tydemania, in Penicillus Sibogie, in the capitulum ofP.duinetosus,&nd in the flabellum of Udotea congliitinata and U. glaucescens; Codiacese 233 verticillate branching also occurs in Tydemania expeditionis, in Boodleopsisand in the capitulum of both spec
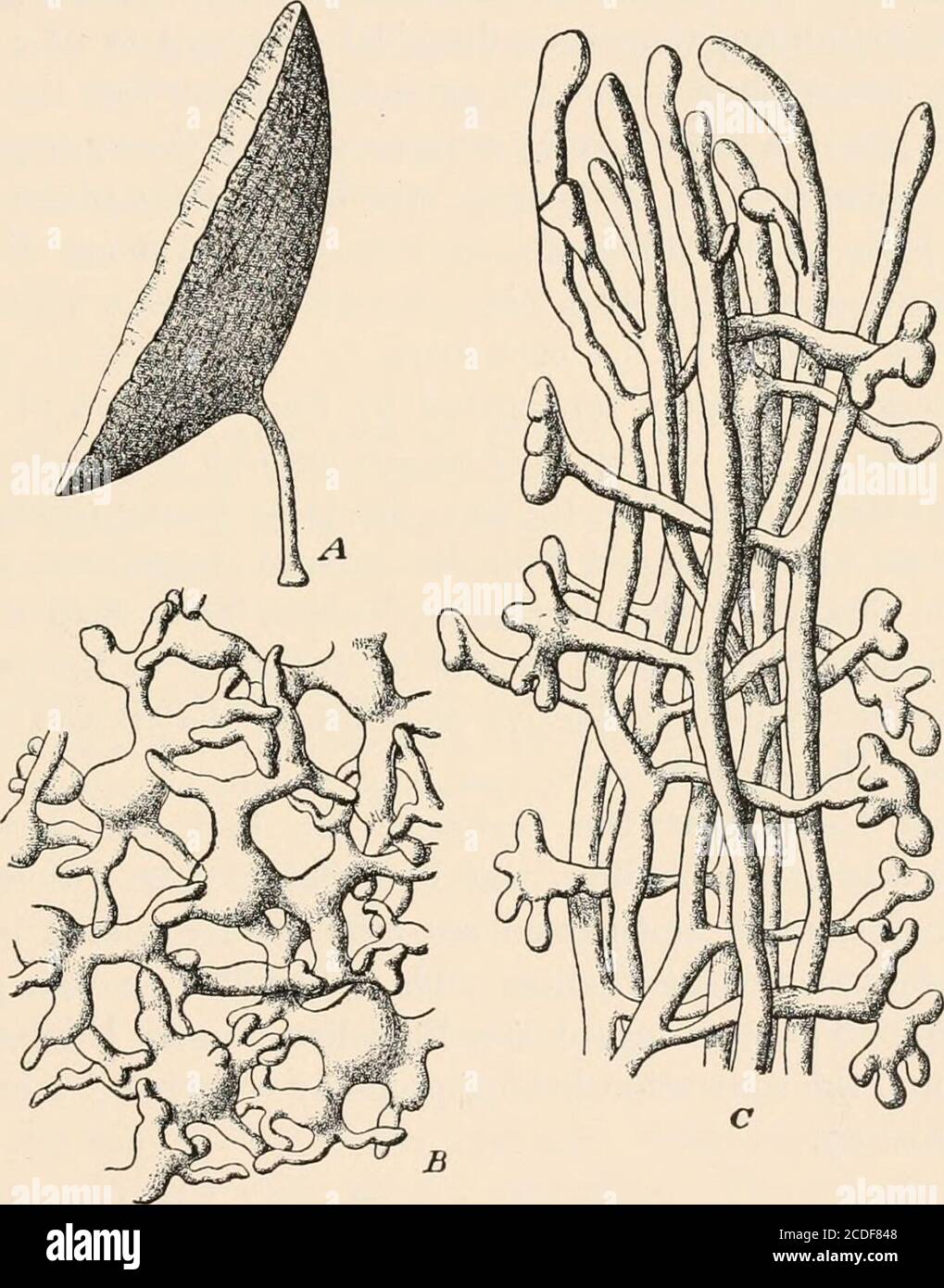
Image details
Contributor:
Reading Room 2020 / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
2CDF848File size:
7.1 MB (387.9 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1400 x 1785 px | 23.7 x 30.2 cm | 9.3 x 11.9 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. Algæ. Vol. I. Myxophyceæ, Peridinieæ, Bacillarieæ, Chlorophyceæ, together with a brief summary of the occurrence and distribution of freshwat4er Algæ . parent-axis. The branching isusually dichotomous, either in one plane or in alternate planes, althoughtrichotomous branching occurs in the basal part of Chlorodesmis comosa, inBoodleopsis, in Tydemania, in Penicillus Sibogie, in the capitulum ofP.duinetosus, &nd in the flabellum of Udotea congliitinata and U. glaucescens; Codiacese 233 verticillate branching also occurs in Tydemania expeditionis, in Boodleopsisand in the capitulum of both species of Rhipocephalus (A. & E. S. Gepp, 11).In addition to the main branches there are often more or less prominentpapillate outgrowths which may occur in great quantity, not infrequentlycohering to form a continuous cortex covering the external surface of thethallus. This cortex may be uncalcified, as in Flabellaria petiolata, orcalcified, as in many species of Udotea, etc. In Cladocephalus there arenumerous pseudo-lateral branches forming an uncalcified labyrinthinecortex (fig. 152 B and C). There are also pseudo-conjugating filaments in. Fig. 152. Cladocephalus excentricus A. & E. S. Gepp. A, plant | nat. size; B, section of theouter portion of the thallus showing the pseudocortex, x 245; C, longitudinal section nearthe apex showing the young branches of the ccenocyte, x 200. (From Wille, afterA. & E. S. Gepp.) Rhipiliopsis, consisting of lateral outgrowths which meet but never coalesce.In the CodiejB the cortex consists of contiguous branch-endings, which in thegenus Pseudocodium are laterally coherent. There is usually a constriction at the base of each branch of a dichotomy, and partial septa are often formed at these points due to the development ofa ring-like ingrowth of the cell-wall. In Callipsyyina this ingrowth is a 234 Siphonales septum with a central aperture, and in Codium and other genera the septaare frequently complete, forming stoppers in various parts of