Info
The oceanic food chain begins with algae, the phytoplankton that is eaten by fish, which are then eaten by larger fish, which are eaten by larger mammals such as seals, dolphins and whales.
At the bottom of the marine food chain are the great white shark (Carcharodon carcharias) and the killer whales (Orcinus orca).
A different feeding strategy is pursued, for example, by saber-toothed blennies, which approach their potential live victims and tear scales, skin and sometimes pieces of the flesh from them at lightning speed.
This strategy is also followed by the cigar shark, which even "takes the white shark to the chest", the cigar shark approaches the white shark and bites it.
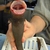
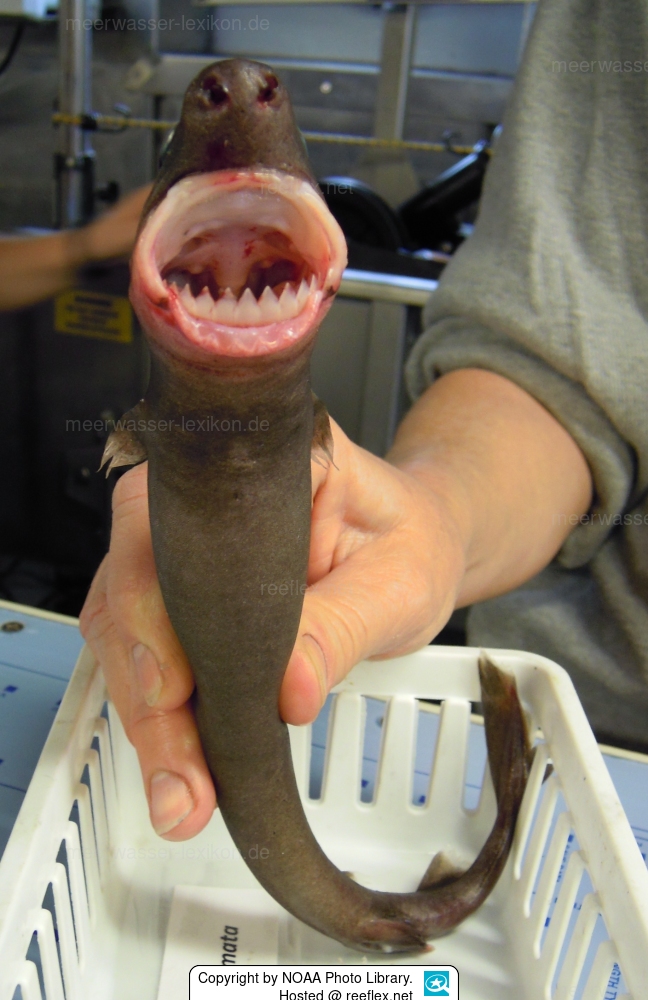
The biting mechanism takes place in such a way that the lower jaw digs upwards into the flesh of the victim when biting, leaving cookie-cutter wounds, hence the English name
"Cookie cutter shark", which could be translated as "cookie cutter shark".
The toothy round mouth of the cigar shark gives a good idea of the size and depth of the bite wounds.
The small cigar shark is not perceived as prey or danger by the giant great white shark, which can grow up to 650cm long, a big mistake.
Synonyms:
Inistius brasiliensis (Quoy & Gaimard, 1824)
Isistius labialis Meng, Zhu & Li, 1985
Leius ferox Kner, 1864
Scymnus brasiliensis Quoy & Gaimard, 1824
Scymnus brasiliensis torquatus Müller & Henle, 1839
Scymnus brasiliensis unicolor Müller & Henle, 1839
Scymnus brasiliensis var. torquatus Müller & Henle, 1839
Scymnus brasiliensis var. unicolor Müller & Henle, 1839
Scymnus torquatus Müller & Henle, 1839
Scymnus unicolor Müller & Henle, 1839
Squalus fulgens Bennett, 1840
Tristius brasiliensis (Quoy & Gaimard, 1824)
Shark bites can be quite lethal to humans, especially the 10 most dangerous shark species are considered and can launch unprovoked attacks from humans: - Great white shark - Bull shark - Tiger shark - Sand tiger shark - Blacktip shark - Bronze shark - Spinner shark - Blue shark - Hammerhead shark - Whitetip shark The bite by a shark is one of the most basic fears of humans, but the number of deaths caused by shark attacks is very low: in 2015 there were 98 attacks by sharks and in 6 cases the attack resulted in a fatal end for humans. In 2016 there were 107 attacks by sharks and in 8 cases the attack resulted in a fatal end for humans. Sources: http://hai.ch/Hai-Infos/Unfaelle/index.html http://www.focus.de/reisen/videos/auch-urlaubsorte-betroffen-schrecklicher-rekord-2016-gab-es-mehr-hai-angriffe-als-je-zuvor_id_6519581.html http://www.spiegel.de/wissenschaft/natur/hai-angriffe-erreichen-2015-rekordhoch-weiterer-anstieg-erwartet-a-1076339.html http://www.zeit.de/2016/37/haie-toetung-tierschutz-surfer
In 2022, there were a total of 108 shark attacks in the USA.
Conversely, however, 100 million sharks were killed by humans. http://www.zeit.de/2016/37/haie-toetung-tierschutz-surfer The risk of being bitten by a shark varies greatly from region to region, with most attacks occurring in Florida, Australia and South Africa. Please be careful not to go into the water with bleeding skin wounds, heed bathing warnings from the authorities and be very careful when using surfboards, as sharks can easily confuse the boards with seals and harbour seals. After shark bites, always call a doctor or / and the rescue service as soon as possible, as heavy bleeding can be life-threatening.
https://worldanimalfoundation.org/advocate/shark-attack-statistics/
At the bottom of the marine food chain are the great white shark (Carcharodon carcharias) and the killer whales (Orcinus orca).
A different feeding strategy is pursued, for example, by saber-toothed blennies, which approach their potential live victims and tear scales, skin and sometimes pieces of the flesh from them at lightning speed.
This strategy is also followed by the cigar shark, which even "takes the white shark to the chest", the cigar shark approaches the white shark and bites it.
The biting mechanism takes place in such a way that the lower jaw digs upwards into the flesh of the victim when biting, leaving cookie-cutter wounds, hence the English name
"Cookie cutter shark", which could be translated as "cookie cutter shark".
The toothy round mouth of the cigar shark gives a good idea of the size and depth of the bite wounds.
The small cigar shark is not perceived as prey or danger by the giant great white shark, which can grow up to 650cm long, a big mistake.
Synonyms:
Inistius brasiliensis (Quoy & Gaimard, 1824)
Isistius labialis Meng, Zhu & Li, 1985
Leius ferox Kner, 1864
Scymnus brasiliensis Quoy & Gaimard, 1824
Scymnus brasiliensis torquatus Müller & Henle, 1839
Scymnus brasiliensis unicolor Müller & Henle, 1839
Scymnus brasiliensis var. torquatus Müller & Henle, 1839
Scymnus brasiliensis var. unicolor Müller & Henle, 1839
Scymnus torquatus Müller & Henle, 1839
Scymnus unicolor Müller & Henle, 1839
Squalus fulgens Bennett, 1840
Tristius brasiliensis (Quoy & Gaimard, 1824)
Shark bites can be quite lethal to humans, especially the 10 most dangerous shark species are considered and can launch unprovoked attacks from humans: - Great white shark - Bull shark - Tiger shark - Sand tiger shark - Blacktip shark - Bronze shark - Spinner shark - Blue shark - Hammerhead shark - Whitetip shark The bite by a shark is one of the most basic fears of humans, but the number of deaths caused by shark attacks is very low: in 2015 there were 98 attacks by sharks and in 6 cases the attack resulted in a fatal end for humans. In 2016 there were 107 attacks by sharks and in 8 cases the attack resulted in a fatal end for humans. Sources: http://hai.ch/Hai-Infos/Unfaelle/index.html http://www.focus.de/reisen/videos/auch-urlaubsorte-betroffen-schrecklicher-rekord-2016-gab-es-mehr-hai-angriffe-als-je-zuvor_id_6519581.html http://www.spiegel.de/wissenschaft/natur/hai-angriffe-erreichen-2015-rekordhoch-weiterer-anstieg-erwartet-a-1076339.html http://www.zeit.de/2016/37/haie-toetung-tierschutz-surfer
In 2022, there were a total of 108 shark attacks in the USA.
Conversely, however, 100 million sharks were killed by humans. http://www.zeit.de/2016/37/haie-toetung-tierschutz-surfer The risk of being bitten by a shark varies greatly from region to region, with most attacks occurring in Florida, Australia and South Africa. Please be careful not to go into the water with bleeding skin wounds, heed bathing warnings from the authorities and be very careful when using surfboards, as sharks can easily confuse the boards with seals and harbour seals. After shark bites, always call a doctor or / and the rescue service as soon as possible, as heavy bleeding can be life-threatening.
https://worldanimalfoundation.org/advocate/shark-attack-statistics/







 NOAA Photo Library
NOAA Photo Library