Info
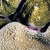
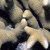
Porites murrayensis
Vaughan, 1918
Similar Species: Porites lobata, which is distinguished by its larger corallites and longer septa. Porites stephensoni has similar corallite characters.
Corals of the genus Porites:
General:
Taxonomists now consider 18 families of stony corals with a total of over 100 genera.
Porites annae, Porites aranetai, Porites arnaudi, Porites astreoides, Porites attenuata, Porites australiensis, Porites branneri, Porites brighami, Porites cocosensis,Porites colonensis, Porites columnaris, Porites compressa, Porites cumulatus, Porites cylindrica, Porites deformis, Porites densa, Porites desilveri, Porites divaricata, Porites echinulata, Porites eridani, Porites evermanni, Porites flavus, Porites furcata, Porites harrisoni,Porites heronensis, Porites horizontalata, Porites latistella, Porites lichen, Porites lobata,Porites lutea, Porites mayeri, Porites monticulosa, Porites murrayensis, Porites myrmidonensis Porites napopora,Porites negrosensis, Porites nigrescens, Porites nodifera, Porites okinawensis, Porites ornata, Porites panamensis, Porites porites, Porites profundus, Porites pukoensis, Porites rugosa, Porites rus, Porites silimaniana, Porites solida, Porites somaliensis, Porites stephensoni, Porites tuberculosus, Porites vaughani.
The two genera Montipora (more than 70 species - Veron 2000) and Acropora (more than 180 species - Veron 2000) are among the most species-rich and numerous.
But besides Montipora and Acropora also Pocillopora, Stylophora, Porites and Psammocora are interesting for aquaristics.
The genus Porites includes the following currently over 50 species.
An identification of the different Porites corals is not easy in every case, if one looks at the pictures on Corals of the World.
A correct identification is done by an examination of the calcareous skeleton and by DNA - examinations.
The care of small polyped stony corals was and is due to the requirements of the corals to water quality and lighting usually far more complex, than that of most LPS corals and zooxanthellate soft corals.
Therefore, only with the possibilities to create a better water quality via skimming and live rock, as well as with better lighting and better calcium supply, the permanent keeping and reproduction came up.
Since keeping SPS corals became an achievable goal for many, zooxanthellate soft corals are hardly in the main focus of most aquarists.
In general it can be stated that Porites corals do not have such high demands on the water quality as e.g. corals of the genus Acropora, but they need a similar amount of light.
As already mentioned for Acropora and Montipora, Porites corals do not only feed on light.
They eat plankton and cover a part of their nutrition with it.
This should not be a problem anymore with suitable feed.
Of course it is advisable to feed at night, after switching off the light, because then the corals will stretch out their polyps to catch.
Important parameters include:
Light:
All small polyp stony corals require very high light levels. Therefore, they should tend to be located at the top of the tank with average lighting.
Heat/Cold:
Corals of the genus Porites will not tolerate water temperatures below 20 degrees or above 30 degrees for long periods of time. Both cases they will acknowledge with bleaching.
Current:
They can tolerate a fair amount of current, though never have the pump outlet pointed directly at a coral. Alternating, more turbulent flow conditions are best.
Water parameters:
Trace elements, (calcium 420-440 mg/L, magnesium 1100-1300 mg/L, KH below 8, strontium 8 mg/L). Water changes: at least 5% a week or 10% a month.
Water quality:
If possible, permanently stable and clear water; if necessary, carbon filtration or ozonization is advisable to remove yellow substances.
The bucket comparison (white containers of the same size, in one freshly prepared water, in the other aquarium water) will quickly show you if your water in the aquarium is as clear as fresh water.
Stony corals do not like to stand in a yellow broth.
Nitrate NO3:
Less than 5 mg/L.
Phosphate PO4:
Less than 0.1 mg/L better even in the range of 0.01 mg/L.
All the mentioned stony corals can be propagated by fragmentation. Let's not forget the aspect of animal - and environmental protection that all coral breeders do by now.
The more offshoots, the less removals in nature. Whereby also there in the years much has done.
Today, corals from aquaculture are preferably offered and sold as offspring.
Vaughan, 1918
Similar Species: Porites lobata, which is distinguished by its larger corallites and longer septa. Porites stephensoni has similar corallite characters.
Corals of the genus Porites:
General:
Taxonomists now consider 18 families of stony corals with a total of over 100 genera.
Porites annae, Porites aranetai, Porites arnaudi, Porites astreoides, Porites attenuata, Porites australiensis, Porites branneri, Porites brighami, Porites cocosensis,Porites colonensis, Porites columnaris, Porites compressa, Porites cumulatus, Porites cylindrica, Porites deformis, Porites densa, Porites desilveri, Porites divaricata, Porites echinulata, Porites eridani, Porites evermanni, Porites flavus, Porites furcata, Porites harrisoni,Porites heronensis, Porites horizontalata, Porites latistella, Porites lichen, Porites lobata,Porites lutea, Porites mayeri, Porites monticulosa, Porites murrayensis, Porites myrmidonensis Porites napopora,Porites negrosensis, Porites nigrescens, Porites nodifera, Porites okinawensis, Porites ornata, Porites panamensis, Porites porites, Porites profundus, Porites pukoensis, Porites rugosa, Porites rus, Porites silimaniana, Porites solida, Porites somaliensis, Porites stephensoni, Porites tuberculosus, Porites vaughani.
The two genera Montipora (more than 70 species - Veron 2000) and Acropora (more than 180 species - Veron 2000) are among the most species-rich and numerous.
But besides Montipora and Acropora also Pocillopora, Stylophora, Porites and Psammocora are interesting for aquaristics.
The genus Porites includes the following currently over 50 species.
An identification of the different Porites corals is not easy in every case, if one looks at the pictures on Corals of the World.
A correct identification is done by an examination of the calcareous skeleton and by DNA - examinations.
The care of small polyped stony corals was and is due to the requirements of the corals to water quality and lighting usually far more complex, than that of most LPS corals and zooxanthellate soft corals.
Therefore, only with the possibilities to create a better water quality via skimming and live rock, as well as with better lighting and better calcium supply, the permanent keeping and reproduction came up.
Since keeping SPS corals became an achievable goal for many, zooxanthellate soft corals are hardly in the main focus of most aquarists.
In general it can be stated that Porites corals do not have such high demands on the water quality as e.g. corals of the genus Acropora, but they need a similar amount of light.
As already mentioned for Acropora and Montipora, Porites corals do not only feed on light.
They eat plankton and cover a part of their nutrition with it.
This should not be a problem anymore with suitable feed.
Of course it is advisable to feed at night, after switching off the light, because then the corals will stretch out their polyps to catch.
Important parameters include:
Light:
All small polyp stony corals require very high light levels. Therefore, they should tend to be located at the top of the tank with average lighting.
Heat/Cold:
Corals of the genus Porites will not tolerate water temperatures below 20 degrees or above 30 degrees for long periods of time. Both cases they will acknowledge with bleaching.
Current:
They can tolerate a fair amount of current, though never have the pump outlet pointed directly at a coral. Alternating, more turbulent flow conditions are best.
Water parameters:
Trace elements, (calcium 420-440 mg/L, magnesium 1100-1300 mg/L, KH below 8, strontium 8 mg/L). Water changes: at least 5% a week or 10% a month.
Water quality:
If possible, permanently stable and clear water; if necessary, carbon filtration or ozonization is advisable to remove yellow substances.
The bucket comparison (white containers of the same size, in one freshly prepared water, in the other aquarium water) will quickly show you if your water in the aquarium is as clear as fresh water.
Stony corals do not like to stand in a yellow broth.
Nitrate NO3:
Less than 5 mg/L.
Phosphate PO4:
Less than 0.1 mg/L better even in the range of 0.01 mg/L.
All the mentioned stony corals can be propagated by fragmentation. Let's not forget the aspect of animal - and environmental protection that all coral breeders do by now.
The more offshoots, the less removals in nature. Whereby also there in the years much has done.
Today, corals from aquaculture are preferably offered and sold as offspring.







 Dr. John Edward Norwood "Charlie" Veron, Australien, Australien
Dr. John Edward Norwood "Charlie" Veron, Australien, Australien