Candida albicans infection in burn wound human skin explants
We are happy to highlight the excellent publication from Christin von Müller et al. recently published in Nature Scientific Reports on Candidiasis infection of burn wounds using GENOSKIN’s NativeSkin® model.
Fungal burn wound infections leading to invasive candidiasis are a big concern reported by burn centers over the world. And however, a difficult one to address because of the lack of accurate models.
Animals are used as models of wounds but fail to replicate molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying fungal infection as seen in humans. Reconstructed skin models have also been used but they miss skin appendages, normal dermal extracellular matrix, or immune cells.
We had the opportunity to exchange with Slavena Vylkova's team. Slavena specifically mentioned that “the easiness of using the Genoskin model has really brought this part of our project to conclusion.”
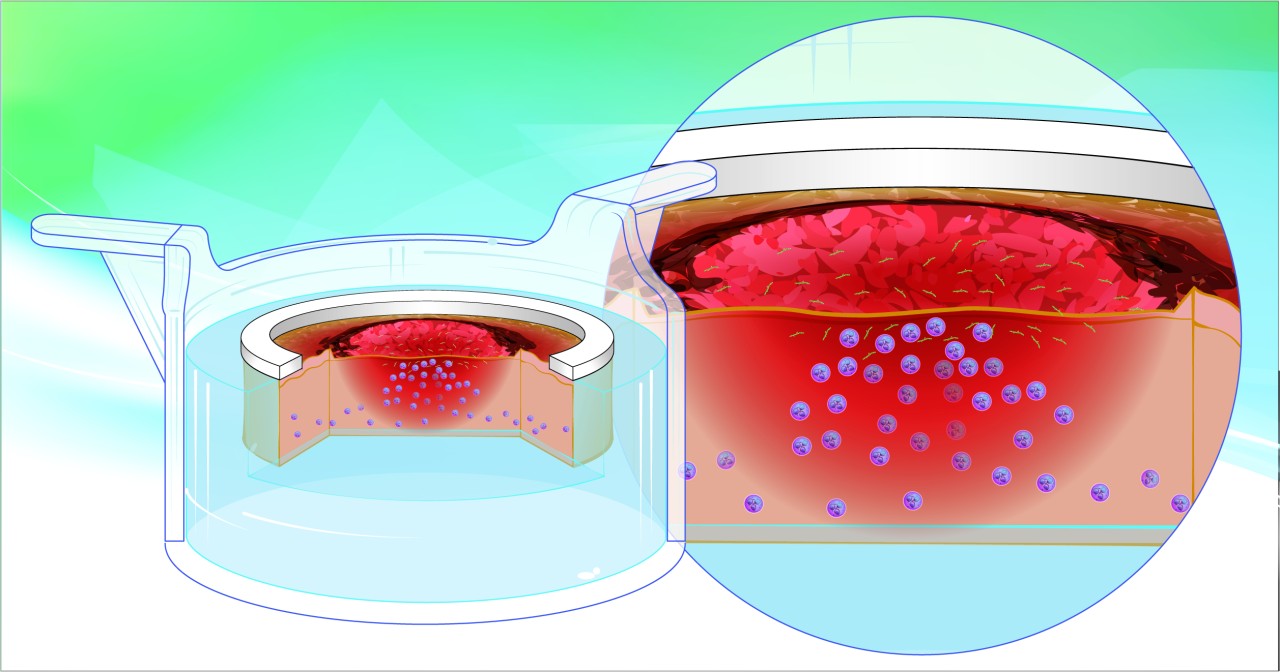
In this study, the authors went through three main steps :
- First, they were able to reproduce a standardized second-degree burn wound human skin model. To do so, they used a NativeSkin® model that they burned with a hot iron at 300˙C during 15s.
- Second, they also demonstrated the ability to produce a Candida wound infection on the model. Best results were obtained by debriding the wound which is an approved clinical treatment in wound care. This allowed fungus to deeper penetrate the dermis.
- Third, they analyzed the presence and behavior of resident neutrophils in the skin model. Using a neutrophil-specific marker, there showed that skin resident neutrophils migrated towards the infection site and accumulated on the edge of the burn after 6 days of the experiment. Furthermore, they demonstrated that when freshly isolated human neutrophils were added to the culture medium, they were also recruited to the infected burn wound site.
In conclusion, @Slavena Vylkova's team validated the use of NativeSkin® to replicate a burn-wound human skin model. They also confirmed that Genoskin skin models were immuno-competent and contained living and functional skin resident neutrophils that can successfully migrate to the burn wound site to counteract C.albicans infection.
A perfect example of how living human skin models helps #accelerateresearch and generate #betterhumandata for #reliableresults !
