Trichophyton mentagrophytes - Laboratory diagnosis
Laboratory diagnosis of Trichophyton mentagrophytes
Laboratory diagnosis of Trichophyton mentagrophytes is done by demonstration of fungal particles such as hyphae, and spores in the specimen.
Samples
Hair
Skin
Nail scrapping
Microscopy
Microscopy (direct microscopy) is performed following KOH preparation to demonstrate fungal particles in the specimen. Spiral hyphae are characteristic of Trichophyton mentagrophytes.
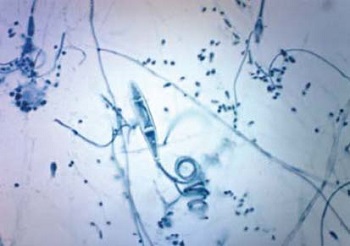
Trichophyton mentagrophytes spiral hyphae (Source: ResearchGate)
KOH preparation
The procedure of KOH preparation for fungal infection diagnosis is as follows.
Procedure
the specimen is placed on a clean, grease-free slide and a drop of 10-20% KOH solution is added to it
the sample is covered with a coverslip and immediately viewed under a microscope
the KOH preparation is examined again after 20 mins
in skin or nail specimens, chains of spores or branching hyphae are seen
in hair specimen, parallel rows of spores are observed inside (endothrix) the hair shaft
* infected hair shaft may also contain air spaces
* skin test does not distinguish active infection

Hair perforation test showing wedge-shaped perforation caused by Trichophyton mentagrophytes (Source: adelaide.edu.au)
Hair perforation test
The hair perforation test is done mostly to distinguish Trichophyton rubrum from Trichophyton mentagrophytes, which are morphologically similar.
Trichophyton rubrum causes only surface erosion of the hair shaft while from Trichophyton mentagrophytes infection results in wedge-shaped perforation.
Procedure
hair specimens (5-10mm in size) are placed in a Petri dish with 20ml distilled water and autoclaved
sterile 10% yeast extract (2-3 drops) is added to the Petri dish
the hair strands are inoculated with small fragments of test fungi that have been grown on SDA
the inoculated hair strands are incubated at 25°C
for up to a month, the inoculated hair strands are examined weekly after the addition of Lacto Phenol Cotton Blue (LPCB)
Wood’s lamp examination
Wood’s lamp examination of Trichophyton mentagrophytes is done by the use of wood’s lamp. This device is used mostly in the diagnosis of fungal infection of the scalp.
Wood’s lamp glass consists of barium silicate containing about 9% nickel oxide. It transmits long-wave UV light with a peak of 365nm. As a result, a distinct fluorescence can be detected on hair infected by dermatophytes.
In Trichophyton mentagrophytes infection, Wood's lamp (blacklight) examination shows bright green to yellow-green fluorescence of hairs.

Culture of Trichophyton mentagrophytes on SDA (Source: Facebook)
Culture
The culture of Trichophyton mentagrophytes is done as a diagnostic step.
The specimen is inoculated onto Sabouraud’s Dextrose Agar (SDA) incorporated with chloramphenicol and cycloheximide and incubated at 25 to 30°C aerobically for 1 to 3 weeks.
The fungi are identified on the basis of colony morphology, color, pigment production, and the presence/absence of microconidia or macroconidia.
The fresh culture was extracted from the agar plate using cellophane tape and placed on a slide containing a drop of Lacto Phenol Cotton Blue (LPCB). The preparation is viewed under a microscope to demonstrate the presence/absence of microconidia or macroconidia.
Trichophyton mentagrophytes colonies may range from granular to powdery. They produce abundant grapelike clusters of subspherical microconidia on terminal branches. In 30% of isolates, the hyphae are spiral while the thin-walled microconidia are smooth, club-shaped, and multiseptate. Each microconidium may measure 6 to 8 µm in diameter and 20 to 50 µm in length.
Urease test
A urease test is done for distinguishing Trichophyton rubrum (urease negative) from Trichophyton mentagrophytes (urease positive).
Procedure
a sterile Christensen’s urea agar is taken and inoculated with test fungi
the test tube is incubated at 25°C for 5 days
if the color of the agar changes to pink in color, it is urease positive
Molecular test
The molecular test used for diagnosis of Trichophyton mentagrophytes is:
PCR-reverse line blot test
real-time PCR test
multiplex PCR test
PCR-ELISA test
MALDI-TOF test